New research on chimps' ground nests may shed light on the development of early humans.
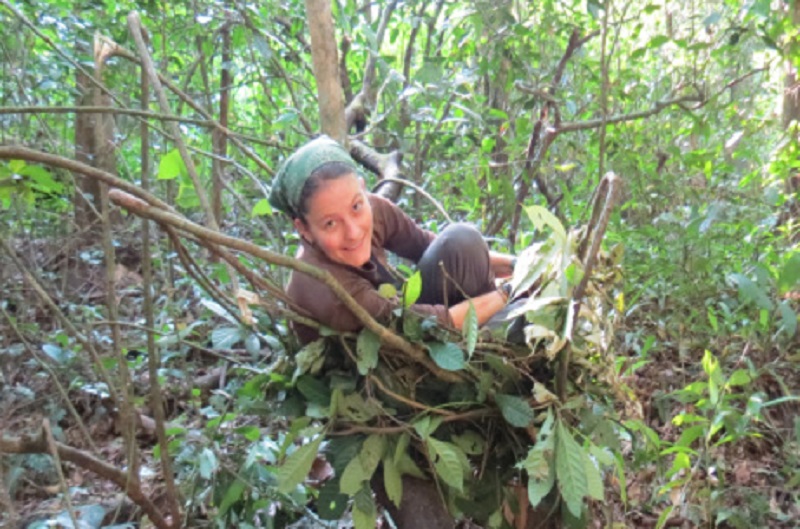
Some chimpanzees regularly sleep on the ground, offering new clues about the ancient transition of early hominins from sleeping in trees to sleeping on the ground, according to research by a Gates Cambridge alumna.
The research by Kathelijne Koops [2006] on chimps in the Nimba mountains of Guinea, West Africa, found that 90 of the 634 sleeping nests she found were constructed on the ground. She and colleagues from Cambridge and Kyoto University, Japan, collected hairs from 46 of the ground nests and subjected them to DNA analysis. This showed at least 12 chimps slept on the ground.
She says the finding could suggest that early hominins who predated Homo Erectus also slept on the ground and that no special evolutionary adaptation was required for the shift. It has previously been thought that hominins only slept on the ground after discovering the ability to light fires and ward off possible predators.
“We believe that, like modern apes, the common ancestor of chimpanzees and humans also slept in the trees six million years ago,” Koops says. “However, these nests are not preserved in the fossil or archaeological record, so it is impossible to study directly the ancient transition from sleeping in trees to building shelters on the ground. Recording this rare behaviour in the chimpanzee, our closest relative, may provide vital clues. The behaviour of these chimpanzees suggests a more deep-seated, gradual transition from tree to ground sleep.”
“These chimpanzees offer a rare opportunity to investigate why a population of wild apes chooses to sleep on the ground,” she adds. “We showed that ground-nesting was not caused by male mate-guarding behaviour, a lack of trees in which to nest, or because of fire. This suggests that our direct ancestors were neither the only, nor the first, species to come down from the trees.”
Researchers suggest that there may be cognitive advantages to sleeping on the ground since it means it is possible to spend more time in REM sleep, which aids memory and cognitive functions. REM sleep is dangerous for tree-sleepers as it paralyses the muscles.
Koops says there could be a feedback loop connecting ground sleeping with cognitive developments like the ability to ward off predators. Her research is published in this week's New Scientist.
Koops did her PhD in Biological Anthropology on the use of tools by chimpanzees in the Nimba mountains with the aid of a Gates Cambridge scholarship. She is currently a junior research fellow at Homerton College, Cambridge.