Paper which marks a breakthrough in glaucoma research wins ophthalmology award.
The work helps not only to bring potential stem cell-based therapies for neurodegenerative disease closer to clinical translation, but also identifies new pathways that could be targeted by pharmaceutical approaches.
Thomas Johnson
A paper by a Gates Cambridge alumnus on a novel mechanism by which stem cell transplantation may help to prevent glaucoma has won top prize at a prestigious ophthalmology awards ceremony.
The research by Thomas V Johnson won first place at the Association for Research In Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO)/Merck Innovative Ophthalmology Research Awards.
Published in the journal Brain, the paper is based on work Thomas did as a Gates Cambridge Scholar as well as subsequent research and is part of a collaboration between the University of Cambridge’s John van Geest Centre for Brain Repair and the National Institutes of Health’s National Eye Institute in the United States.
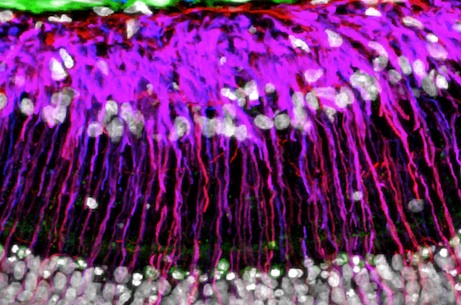
Dr Johnson’s research focuses on glaucoma, a neurodegenerative disease of the optic nerve, the “cable” which carries visual information from the retina in the eye to the brain. Glaucoma causes the progressive loss of retinal ganglion cells, which make up the optic nerve, eventually leading to vision loss and potentially blindness. Previous research by Dr Johnson showed that transplantation of stem cells from the bone marrow into the eye could protect the optic nerve in a rodent model of glaucoma, but the mechanism by which that protection occurs was unclear.
It demonstrates that bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells produce and secrete a large number of proteins that each individually help to protect retinal ganglion cells from stress and cell death. Together, the additive effect of these proteins (the stem cell “secretome”) appears to confer potent neuroprotection. Dr Johnson’s team identified one particularly strong neuroprotective factor, platelet-derived growth factor or PDGF, that, when injected into a glaucomatous eye on its own, protected almost 90% of the optic nerve fibres that otherwise would have degenerated.
Dr Johnson [2006], who did his PhD in Brain Repair, says: "The work helps not only to bring potential stem cell-based therapies for neurodegenerative disease closer to clinical translation, but also identifies new pathways that could be targeted by pharmaceutical approaches."
Dr Johnson is currently based at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.












