Ramit Debnath is co-author of a paper on how to ensure energy policy research serves local needs
Bridging the North-South divide in energy policy research is critical in avoiding future energy crisis. We need more localised solutions through global partnerships.
Ramit Debnath
Energy policy in the Global South needs to be rooted in the local context, according to a new paper, co-authored by a Gates Cambridge Scholar, which outlines ways of bridging the Global North-South research divide.
The paper, Bridging the divide in energy policy research: Empirical evidence from global collaborative networks, is published this week in Energy Policy.
Co-authored by Gates Cambridge Scholar Ramit Debnath [2018], it argues that energy policy design and technology transfer needs to be rooted in local knowledge rather than be seen as a handout from Global North research organisations. And it says policymakers in the Global South should make institutional efforts to be aware of the extent to which the policies they adopt reflect Northern frameworks and perspectives and how much of that is applicable to their specific contexts.
On research funding and infrastructure, the paper notes that the flow of funds from the Global North to the Global South needs to be rethought so that the relevance of energy policy design to the local context is prioritised and local researchers and indigenous knowledge transfer are foregrounded.
The paper outlines how China offers a potential alternative knowledge production process for emerging economies. It states: “China shows it is possible to establish energy research knowledge production processes which do not rely on high income countries to undertake the research. Recognising that much Chinese research is domestically focused, this enables greater contextual embeddedness of the researcher…”
And it says improving the data infrastructure of countries in the Global South is vital for effective contextualised policy design. Another key issue is the importance of experiential learning between local partners and funding agencies. The paper says this should be encouraged through co-development of methods and experiments that reflect the grounded realities of the research being undertaken.
Ramit, now Inaugural Cambridge Zero Fellow at the University of Cambridge and Visiting faculty associate in computational social science at Caltech, said: “Bridging the North-South divide in energy policy research is critical in avoiding future energy crisis. We need more localised solutions through global partnerships, and we call for this co-production of knowledge through this work.”
*Picture credit: Wind farm in Xinjiang, China, courtesy of Wikipedia.
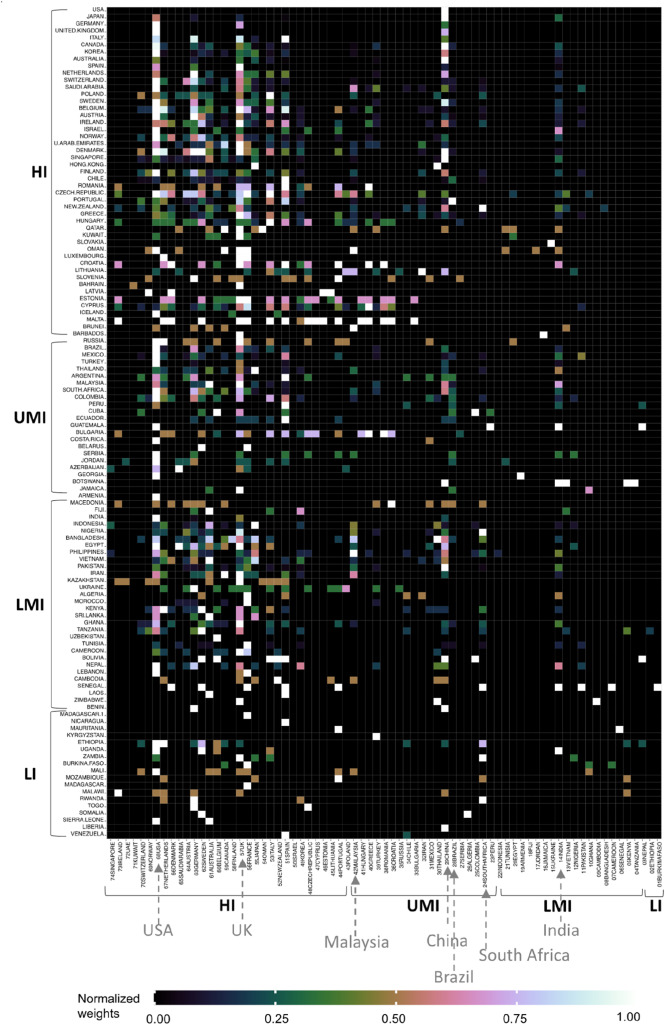
The image below shows energy policy research production as per the GDP of the countries.