Zhiyu Chen scoops history of science & medicine prize for essay on evidence of knowledge exchange between the Ming-Chinese and Iberian conventions in the 16th century
A Gates Cambridge Scholar has won a prestigious essay competition about the history of early science with a treatise on evidence of knowledge exchange between the Ming-Chinese and Iberian conventions in the 16th century.
The essay competition was run by the Early Sciences Forum of the History of Science Society and the Early Science and Medicine journal and was open to early career scholars focusing on early science, medicine, technology, and other forms of natural knowledge across the globe before 1800.
Zhiyu Chen [2023], who is doing a PhD in the History and Philosophy of Science, was told of the award last week and took part virtually in a celebration of the prize at the History of Science Society’s Annual Meeting in Portland.
Her essay, titled “Entangled Imaginations: The Boxer Codex, Colonial Visions, and Cross-Cultural Knowledge in the Late-Sixteenth-Century Western Pacific Rim”, will be published as an article in Early Science and Medicine.
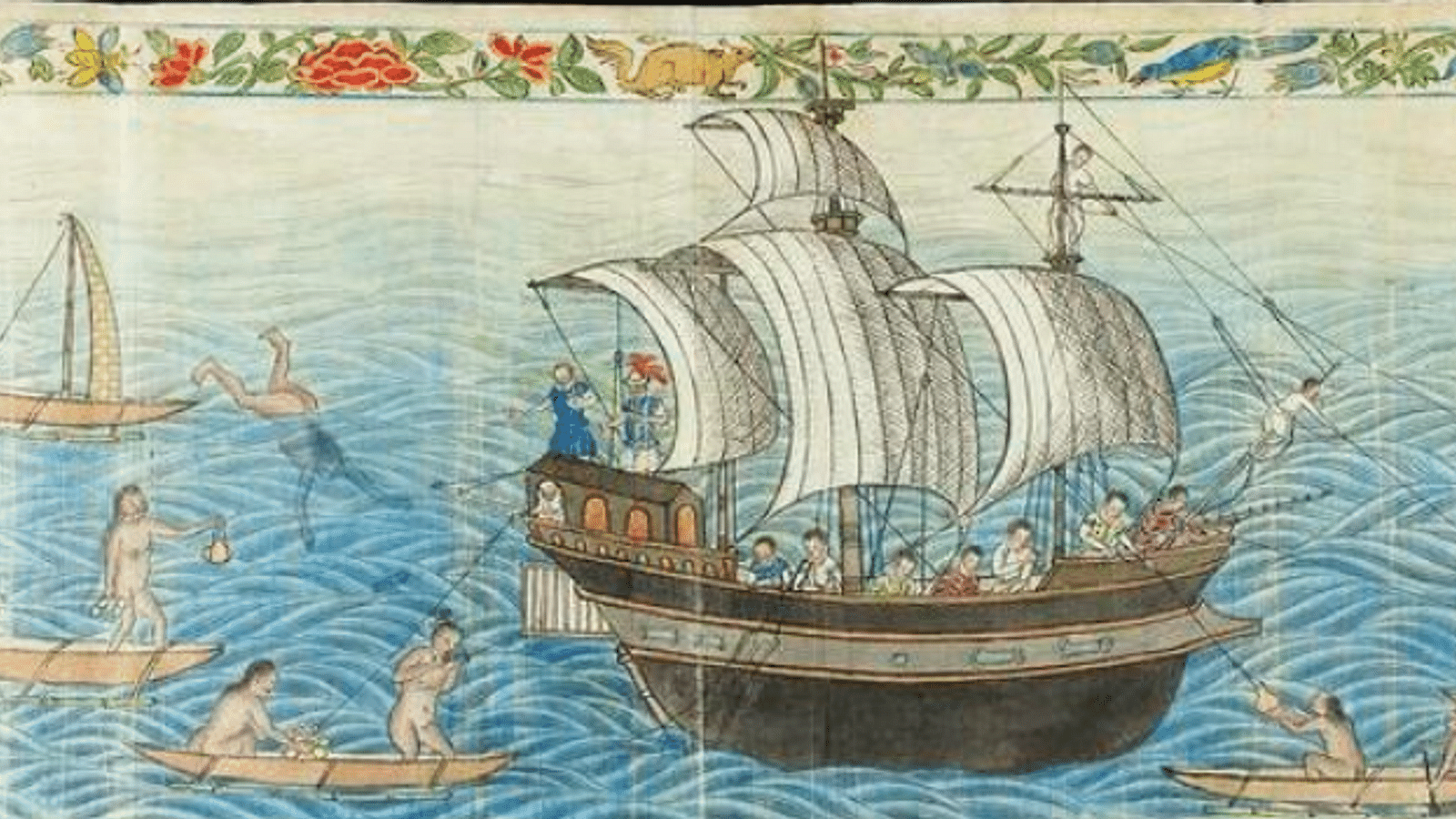
It was praised for its analysis of one of the most essential texts on the history of the Pacific, and knowledge about that region, the Boxer Codex, a Spanish-language manuscript produced in late 16th-century Manila and for how it showed how “the Boxer Codex represents a case of epistemological exchange between the Ming-Chinese and Iberian conventions”.
The essay shows that, through the depiction of deities and fantastical creatures, the Codex’s creators reveal their active entanglement with Ming China, suggesting both the power of and limits to the agency, judgment and biases of various intermediaries. It argues: “Far from being a venue of commensurability, European authority was preferred and asserted in the Boxer Codex.”
As such “the manuscript thus reflects Spanish knowledge-making in a world where their presence was precarious”. It reveals, say the judges, “the contingency surrounding the transmission of knowledge and the complexity of local contexts that must not be overlooked in writing global histories of science”.