Veronika Mantziou co-authors a review which highlights how pluripotent stem cells can advance research on early human development.
In this review article, we discuss what we know about the early stages of human development and particularly human gastrulation, a process during which the body plan is established.
Veronika Mantziou
Pluripotent stem cells-based models serve as an excellent tool to study early human development, given that legislation forbids using human embryos to do so, according to a review.
The review, published in the journal Developmental Biology, is co-authored by Gates Cambridge Scholar Veronika Mantziou [2019], who is doing a PhD in Developmental Biology.
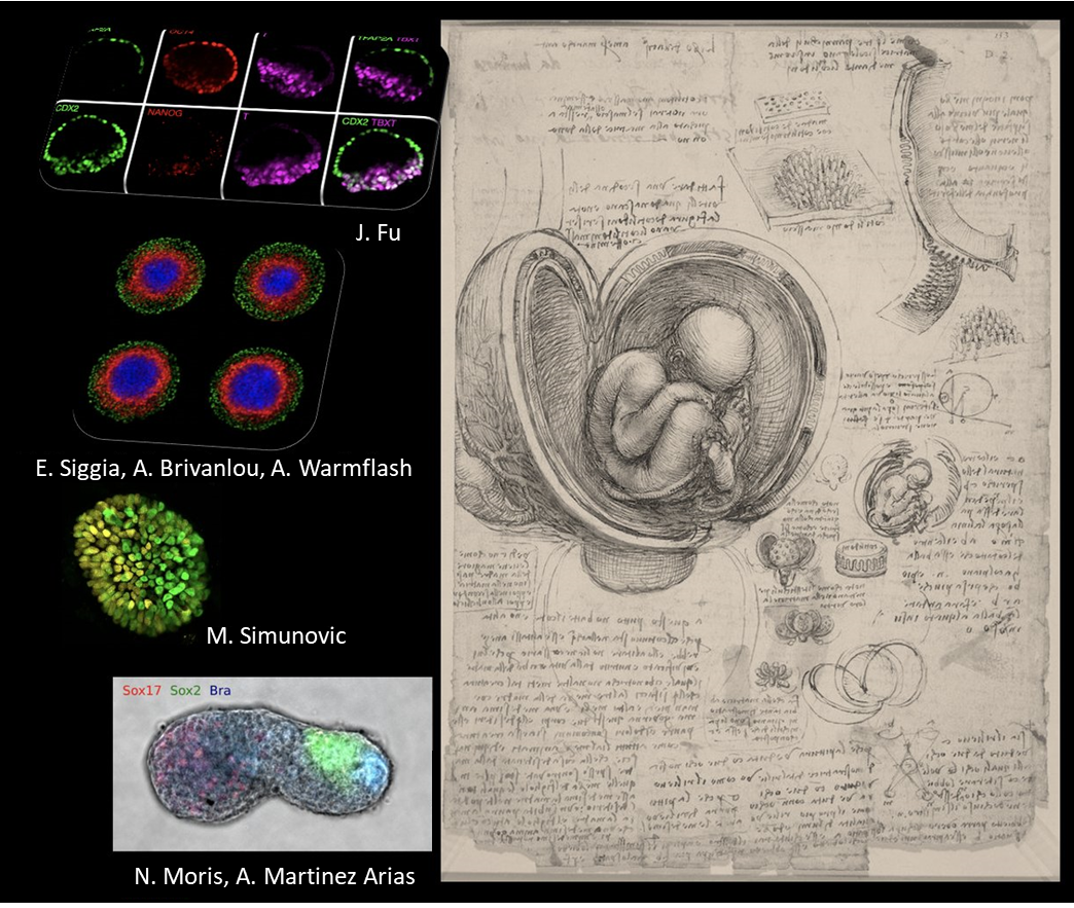
The study, Human gastrulation: the embryo and its models, starts from the point of the technical and ethical constraints that make the study of early human development challenging – particularly the period following the first three weeks of development when the fundamental aspects of the body plan are established. The ‘14-day rule’ restricts human embryo research to the first 14 days after fertilisation. As such, there have been no experimental studies beyond this stage – even though human gastrulation, the process during which the body plan is established, takes place in this period.
Over the years, mutagenesis programmes have established the mouse as the reference organism for mammalian development. Nevertheless, the review underlines that, due to the existence of significant species-specific differences, it is clear that studying the mouse is not sufficient to understand what happens in human development.
In the absence of legislation permitting the study of early stage embryo development, the review highlights that pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) are beginning to provide insights. PSCs are cells that have the capacity to self-renew by dividing and to develop into the three primary germ cell layers of the early embryo.
Veronika says: “In this review article, we discuss what we know about the early stages of human development and particularly human gastrulation, a process during which the body plan is established. We look at how it differs from the mouse and what we can learn from human PSC models in order to take research on early human development forward.”
*Picture credit: Professor Alfonso Martinez Arias












